What is Explosion Proof Lighting?
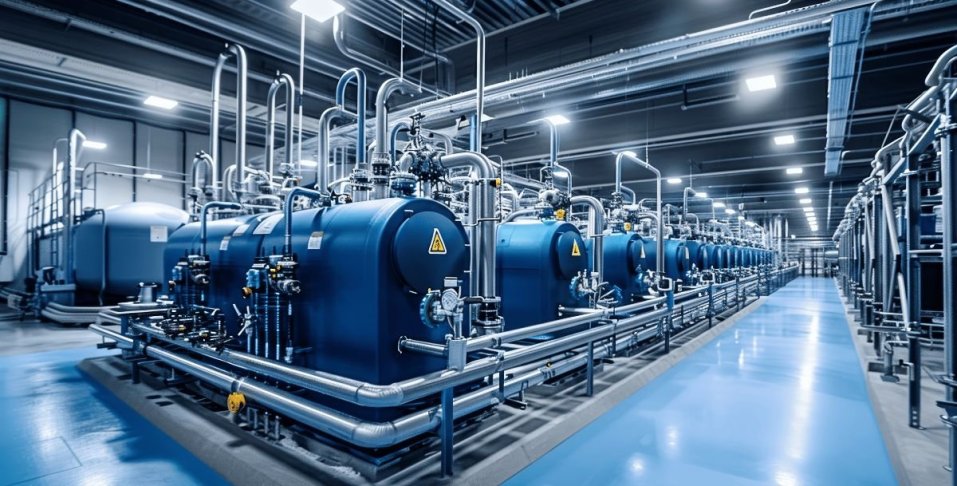
Explosion proof lighting is specially designed to prevent the ignition of hazardous materials in environments where explosive gasses, vapors, or dusts are present. These lights are built with durable, robust materials and sealed enclosures that contain any potential sparks or flames, ensuring they do not come into contact with the surrounding explosive atmosphere.
Explosion proof lighting is commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and manufacturing. It ensures both safety and compliance with regulatory standards in hazardous areas.


Classification Systems for Hazardous Locations
The NEC uses two main systems to classify hazardous areas: the classes/divisions/groups system and the zones/groups system. While various organizations have developed their own classifications, the NEC is the most widely recognized in the U.S.
Classes, Divisions, and Groups
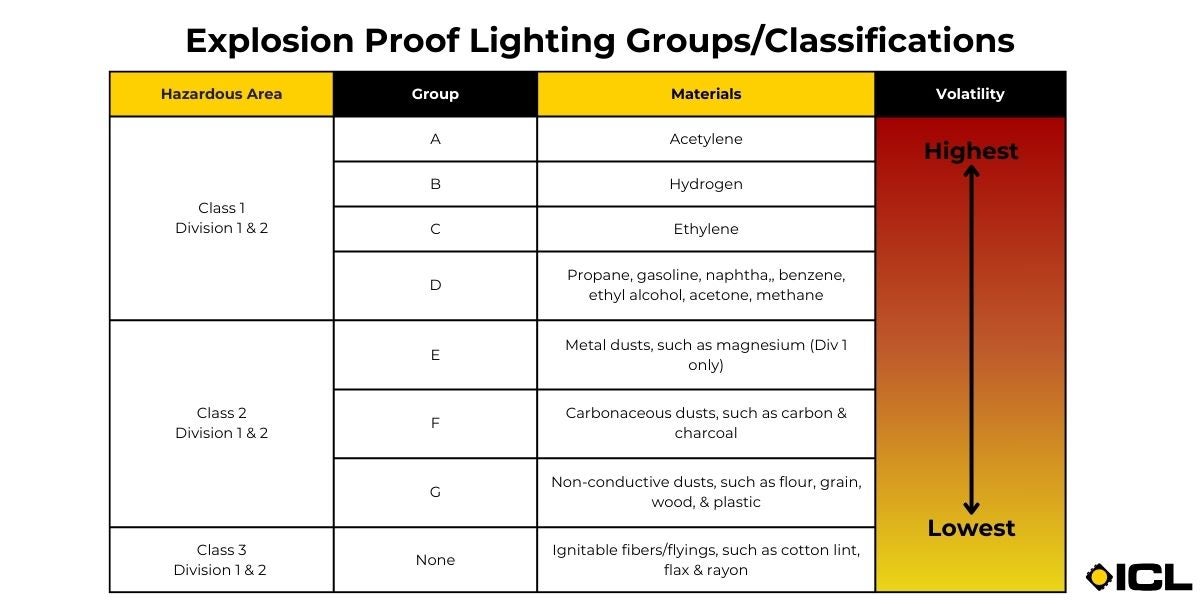
Detailed in NEC Article 500 from the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), this system categorizes hazardous areas based on the materials present (Classes), the likelihood of hazardous concentrations (Divisions), and the specific substances involved (Groups). The key divisions are:
- Class I, Division 1: Areas where flammable gasses or vapors are present during normal operations.
- Class I, Division 2: Locations where such gasses or vapors are not normally present but may exist under abnormal conditions.
- Class II, Division 1: Areas where combustible dust is present during normal conditions.
- Class II, Division 2: Locations where combustible dust is not typically present during normal operations.
- Class III, Division 1: Facilities handling nonmetal fibers or flyings under normal conditions.
- Class III, Division 2: Areas where nonmetal fibers or flyings are stored or handled but not actively manufactured.
Groups of Explosion Proof Lights
OSHA further classifies hazardous locations by dividing them into seven groups based on the properties of the present substances:
- Class I Groups A to D: Gasses, such as acetylene (Group A), hydrogen (Group B), ethylene (Group C), and propane (Group D).
- Class II Groups E to G: Dusts, including metal dusts (Group E), carbonaceous dusts (Group F), and non-conductive dusts like wood, grain, and flour (Group G).

Zones and Gas Groups
Zones define the likelihood and duration of the presence of explosive atmospheres and help classify the level of hazard in a particular area. These are based on international standards, specifically the IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) and ATEX directives, and are commonly used in Europe and other regions.
- Zones 0, 1, and 2: For gasses and vapors, Zone 0 represents continuous or long-term exposure, Zone 1 indicates potential exposure, and Zone 2 denotes rare exposure under normal conditions.
- Zones 20, 21, and 22: For dusts and fibers, with similar distinctions based on the frequency and duration of exposure. Zone 20 represents continues presence of explosive dust. Zone 21 indicates the likely presence of explosive dust during normal operations. Zone 22 means there is the occasional presence of explosive dust.


Temperature Classification (T-Classes)
Temperature classification, or T-Class, is a key factor in explosion proof equipment design. The classification indicates the maximum surface temperature of equipment under standard conditions, typically with an ambient temperature of 40°C (104°F). T-classes range from T1 to T6, with lower classes (e.g. T1) allowing higher surface temperatures:
- T1 Class: 450°C (842°F)
- T2 Class: 300°C (572°F)
- T3 Class: 200°C (392°F)
- T4 Class: 135°C (275°F)
- T5 Class: 100°C (212°F)
- T6 Class: 85°C (185°F)
These classifications help ensure equipment does not reach a temperature that could ignite hazardous materials in the environment.
To ensure safety in these environments, all equipment, including lighting, must be certified for the specific class, division, group, or zone in which it will be installed. This includes markings for intrinsically safe equipment, which is designed to prevent sparking and avoid storing enough energy to ignite a hazardous atmosphere.
Requirements for Explosion Proof Lights
Lighting used in hazardous environments must adhere to strict standards to ensure safety. The National Electrical Code (NEC) defines hazardous locations as areas where the presence of flammable gasses, vapors, or dust creates a risk of fire or explosion.
Explosion proof fixtures have durable, impact- and corrosion-resistant casings made from materials like aluminum, stainless steel, or fiberglass, with shatterproof lenses for added protection.
Copper-free aluminum is commonly used for its non-sparking, lightweight, and heat-dissipating properties, further minimizing the risk of ignition. These fixtures are designed to prevent ignition by sealing out flammable substances and feature thermal control mechanisms like copper-free housings and heat sinks to keep them cool and reduce the risk of fires or explosions in hazardous environments.
Types of Explosion Proof LED Lights
Explosion Proof High Bay
Overview: Designed for use in hazardous locations, explosion proof high bays are ideal for areas with high ceilings, such as warehouses, manufacturing plants, and industrial facilities with a risk of explosive gasses or dust. These lights provide powerful illumination and are engineered to withstand harsh environments.
Applications & Features: Explosion proof high bays are recommended for high-risk areas such as oil refineries, chemical plants, and industrial warehouses due to their high lumen output and corrosion resistance.


Explosion Proof Low Bay or Linear Light
Overview: Similar to high bays, explosion proof low bays, which can also be called explosion proof linear lights, are used in hazardous areas. However, they are designed for spaces with lower ceilings (typically under 20 feet) and provide focused, energy-efficient lighting for more confined workspaces.
Applications and Features: Explosion proof low bays are commonly used in storage rooms, loading docks, and industrial workspaces with lower ceilings, especially in areas with volatile chemicals or flammable vapors. These compact, robust fixtures provide sufficient light intensity for safe operation in smaller hazardous areas while maintaining energy efficiency.


Explosion Proof Flood Light
Overview: Explosion proof flood lights are built to provide broad, intense lighting over large areas, such as outdoor industrial zones or open spaces in hazardous environments. They can illuminate wide areas without igniting hazardous gases or dust.
Applications and Features: Explosion proof flood lights are used in large outdoor hazardous environments like oil rigs, fuel loading stations, and mining operations to ensure maximum visibility for safe operation. Typically installed on poles or walls to cover vast areas, these lights feature durable, weather-resistant construction, wide beam spread, and are built to withstand extreme temperatures and corrosive materials.


Explosion Proof Emergency Lights
Overview: Explosion proof emergency lights are critical in providing safe illumination during power outages or emergencies in hazardous areas. They ensure safe evacuation or continued operation in environments where explosive gasses or dust may be present.
Applications and Features: Emergency lights are commonly used in chemical processing plants, oil refineries, and other industrial locations with hazardous materials. Designed to activate automatically during emergencies, they feature battery backup systems, durable enclosures, and reliable performance during power failures, ensuring safety in critical situations.




Hazardous Locations Certifications and Standards
UL Certifications & Standards
UL Solutions, formerly Underwriters Laboratories, is a prominent authority on safety standards in the United States. They develop standards and testing procedures that enable the classification and certification of products and components. The certification process is performed by UL and other certifying bodies that follow UL's standards, such as Electrical Testing Labs (ETL) and CSA. Products with UL Certification or UL Listing have passed all required testing for their intended installation and use. To ensure compliance, look for UL 844 certification for lighting products certified for use in hazardous locations.
UL Certified
The “UL Certified” mark indicates that lighting products comply with stringent safety standards, protecting against electrical, fire, and injury risks. This certification, upheld through ongoing compliance and regular inspections, is a reliable mark of quality for both manufacturers and consumers. It provides manufacturers with confidence in their products' quality and assures consumers that their lighting choices are unlikely to present safety hazards.


UL Listed
The "UL Listed" mark indicates that lighting products and accessories, whether individual components or complete units, are designed for installation without modification. This designation applies to both entire fixtures and specific components, such as ballast-compatible bulbs.