Table of Contents
- Is There a Difference Between Power Supplies and Power Adapters?
-
What is the Difference Between Alternating and Direct Current?
-
How Do I Figure Out What Input and Output Voltage I Need?
-
What Causes Voltage Drop in My Power Supply?
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
-
How Can I Protect My Power Supply From Electrical Surges?
- How Can I Tell if My Power Supply Isn’t Working Correctly?
-
What Causes Overheating in Power Adapters or Supplies?
-
Why Is a Power Supply Causing My Lights to Flicker?
-
What Causes Buzzing Noises in My Power Supply and How Do I Fix It?
1. Is There a Difference Between Power Supplies and Power Adapters?
Yes, ‘Power supply’ is the overarching term for devices converting electricity from one form to another. These are common with products that require a consistent voltage to operate. Power supplies are commonly used in medical devices, aircraft, and televisions. Power adapters are a subset of power supplies, usually referring to low-wattage AC/DC power supplies that power small electrical devices such as phones, laptops, tablets, and other wall plug-in devices.
2. What is the Difference Between Alternating and Direct Current?
Alternating current (AC) is the continuous oscillation between minimum and maximum current within the circuit. When the voltage is positive, the current will flow in one direction, and then reverse when the voltage is negative. Alternating current is easily transmitted and converted for power distribution, efficiently delivering electricity from power plants to homes and businesses. Alternating current is most commonly used as the input power for standard or high-voltage applications located in a standard residence or commercial and industrial facilities.
Direct current (DC) occurs when there is a steady flow of current within the circuit. The unidirectional current delivers a constant energy supply with the polarity remaining the same. Direct current is used with low-voltage applications or by anything powered by batteries. The chemical reaction within a battery generates direct current, meaning direct current is also used to charge anything with a battery, such as laptops and cell phones.
3. How Do I Figure Out What Input and Output Voltage I Need?
Input voltage is the amount a power supply can take in from the source. Consider the power supply's purpose to determine the appropriate input voltage. For example, 120 VAC might be more common for residential applications, whereas 240 VAC is usually better for commercial applications.
Output voltage is what the power supply releases to the application and installing incompatible output voltage can cause malfunction. A 12V power supply can be used for smaller appliances such as laptops, but a 48V higher-voltage power supply is generally needed for larger applications, such as electric golf carts.
4. What Causes Voltage Drop in My Power Supply?
Voltage drop occurs when a current begins lowering due to there not being enough voltage to power the electrical chain. Two types of voltage drop might occur when powering long runs:
-
A power supply (i.e., Magnetic) output voltage drops when a larger load is applied. Electronic power supplies provide a more consistent output voltage over the full power output range.
-
As you get further away from the power supply, there isn’t enough current to power the application.
Voltage drop is inevitable, but you can limit the effect by:
-
Connecting the power source as close to the power supply as possible. If a long run of wire is required to connect to the power supply.
-
Select a wire gauge appropriate for the length of the wire (e.g., using an 18awg wire since it’s wider than a 22awg wire).
-
Measure the power you need. The device should only require 80% of the power supply's energy.
-
Using wire connectors to provide better connections and reduce the risk of incompatible wire lengths.
-
Calculate the full electrical run to ensure enough power; this includes accounting for all products involved.
For more information on voltage drop, visit this blog by our affiliate Super Bright LEDs.
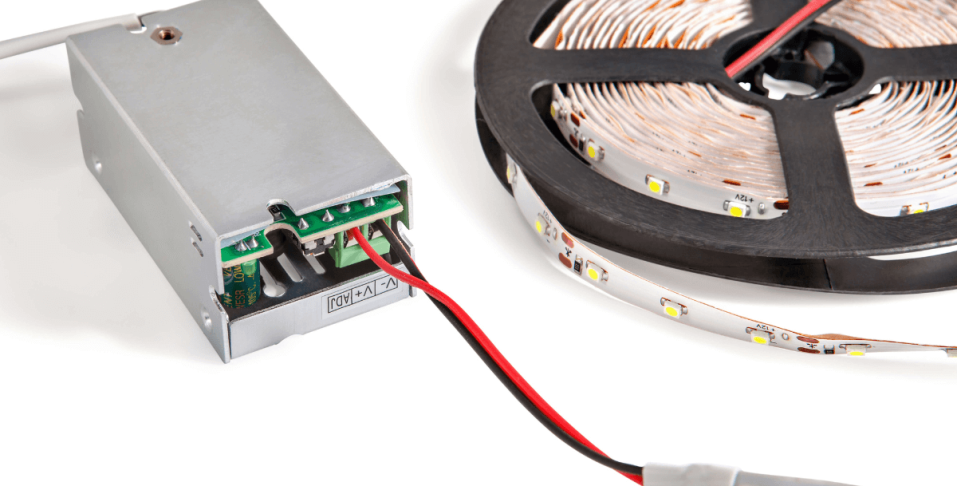
5. How to Wire a Power Supply
Each installation might vary. The following four steps can get you started:
-
Ensure the main power source or circuit breakers are switched off before performing any installation or wiring procedures.
-
Locate the negative and positive wires on the output side and connect them to the electrical system's corresponding positive and negative wires.
-
Plug in or connect the power supply's line, neutral, and ground (if applicable) input wires to the AC power source. For the proper wiring procedure, refer to the product's wiring diagram.
-
Turn on the power source and confirm that the device is functioning correctly.
6. What is an LED Driver?
An LED driver is a power supply designed to power LEDs and other technologies. The product line includes constant current and constant voltage options, as well as dimmable and waterproof options. Our drivers have undergone extensive testing in our in-house lab to ensure you get high-grade drivers. We also have emergency backup drivers to continue delivering battery power during an outage, offering at least 90 additional minutes.
Read this blog from our affiliate, Super Bright LEDs, for more information on emergency backup drivers.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
1. How Can I Protect My Power Supply From Electrical Surges?
Power surges occur when the voltage suddenly increases. Fix surges by ensuring up-to-date wiring or installing surge protectors on the power supply. Surge protectors catch a voltage increase and redirect the extra voltage to the ground wire. Various types of surge protectors are available to accommodate different situations.
2. How Can I Tell if My Power Supply Isn’t Working Correctly?
There are various indicators of issues in a power supply. The most common are listed below. Each indicator will be explained in more depth later.
-
Overheating
-
Flickering
-
Buzzing Noise
3. What Causes Overheating in Power Adapters or Supplies?
The most common factor causing overheating is the environment the electrical device is installed. A power supply installed in a space subject to heat, debris, or poor airflow is more prone to overheating. Improper wattage is another factor of overheating, where the maximum load shouldn’t be greater than 80% of the power supply capacity. Verify the needed voltage or wattage before installing.
4. Why Is a Power Supply Causing My Lights to Flicker?
Flickering lights can signal a failing component in the power supply, incompatibility with the light, or the power supply is of poor quality. Poor quality often indicates cheap construction, incorrect wattage output, or fluctuating voltage. However, flicker doesn’t occur only in lighting. Voltage fluctuations can also cause flicker in laptops, medical devices, and various electronic applications. Power supplies causing flickering should be replaced.
For help selecting a power supply, contact a product support specialist at 866-201-2238.
5. What Causes Buzzing Noises in My Power Supply and How Do I Fix It?
Incompatible dimmers or poorly produced or loosely assembled parts can create buzzing noises. Check if the power supply is placed on a rough surface or in an area prone to movement. If the buzzing continues, purchase a new, certified power supply. Super Bright LEDs offers multiple UL, ETL, and FCC-listed options.