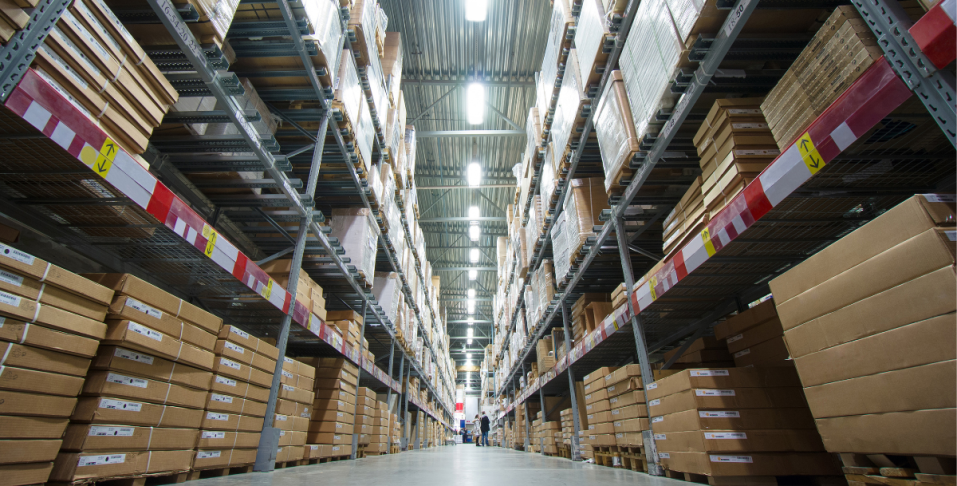
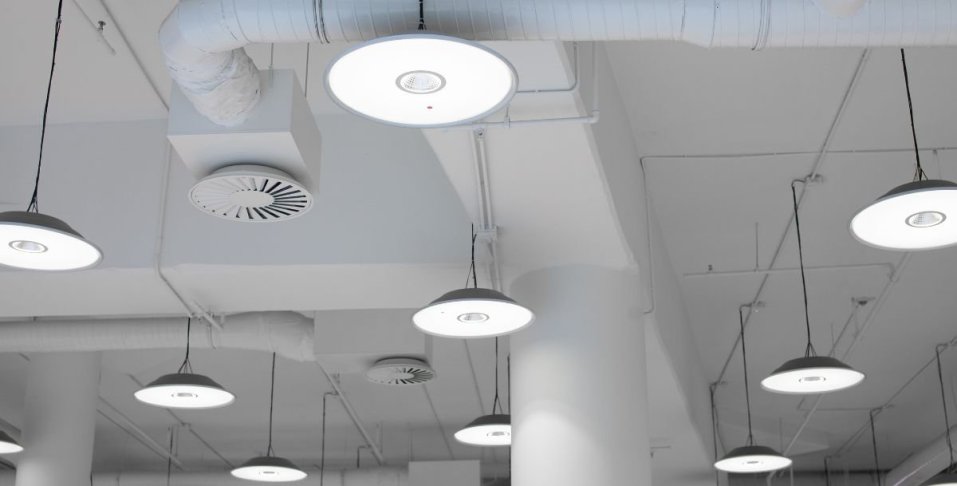
Bay lighting systems ensure uniform lighting across large, expansive spaces. Commonly used in warehouses, factories, retail stores, gyms, and auditoriums, these fixtures enhance safety and productivity by providing consistent, glare-free illumination. Designed for optimal performance in demanding environments, bay lighting reduces dark spots, improves visibility, and supports energy efficiency, making it an essential solution for commercial and industrial applications.
Bay lights come in two main types: high bay lights, designed for ceilings over 20 feet, and low bay lights, suited for ceilings below 20 feet. Both types offer features tailored to their specific applications, ensuring optimal illumination.
Key Features of Bay Lights
-
High Lumen Output: Designed to produce bright, consistent light suitable for large areas.
-
Energy Efficiency: LED technology is used to reduce energy consumption and prolong its lifespan.
-
Durability: Built to withstand challenging conditions, including dust, moisture, and temperature variations.
-
Even Illumination: Engineered to provide even lighting over large spaces with minimal glare.
What Are LED High Bay Lights?
LED high bay lights are designed for spaces with ceilings 20 to 45 feet or higher. They offer powerful, focused illumination to effectively cover large, vertical areas. They are a key solution for environments requiring bright, consistent lighting from significant heights.
Key Features of High Bay Lights
-
Lumen Output: High brightness ensures effective illumination from greater heights.
-
Beam Angle: Narrow flood angles (60°-120°) focus light downward to reduce waste.
-
Light Types: Includes UFO high bays, linear high bays, corn bulbs, and high bay bulbs.
-
Accessories: Reflectors or lenses optimize light direction and minimize glare.


Common Industrial LED High Bay Lighting Applications
Used in warehouses, manufacturing facilities, and gymnasiums, industrial LED high bay lighting provides reliable and efficient lighting for large, open spaces.
Advantages of High Bay Lights
-
Provide broad, powerful lighting for high ceilings.
-
Efficient for large vertical areas, reducing energy waste.
-
Minimize shadows in spaces with tall shelving or equipment.
What Are LED Low Bay Lights?
LED low bay lights are lighting fixtures specifically designed for spaces with ceilings under 20 feet. These lights are optimized to provide even, dispersed illumination for smaller or more confined areas, making them ideal for settings where close-range lighting is required. Low bay lighting includes, but is not limited to, strip lights, recessed lighting, track lighting, panel lights, troffers, and tube lights.
Key Features:
-
Lumen Output: Moderate brightness to suit shorter distances and avoid excessive glare.
-
Beam Angle: Wider flood angles (120° or more) ensure uniform light distribution across the area.
-
Light Types: Include strip light fixtures, panel lights, wraparound fixtures, troffers, and LED retrofit kits.
-
Mounting Options: Typically installed with a surface mount, pendant mount, or suspension mount.


Common Industrial LED Low Bay Lighting Applications
Industrial LED Low bay lighting is commonly used in retail stores, garages, storage areas, and smaller warehouses, where even close-range lighting is essential.
Advantages of Low Bay Lights
-
Deliver well-distributed, glare-free illumination for low ceilings.
-
Reduce harsh shadows in tight or confined spaces.
-
Offer a cost-effective solution for areas with lower lighting needs.
Comparing High Bay and Low Bay Lights
When comparing high bay and low bay lights, multiple factors must be considered to determine which fixture will best suit the space and its requirements.
Ceiling Height
-
High Bay: Optimal for high ceilings above 20 feet.
-
Low Bay: Suited for ceilings 20 feet or lower.
The primary distinction between high bay and low bay lights lies in the ceiling height they are designed for. High bay lights are optimized for ceilings above 20 feet, ensuring bright and focused illumination even in expansive spaces. In contrast, low bay lights are best suited for ceilings 20 feet or lower, providing even lighting for close-range applications.
Applications
-
High Bay: Ideal for spaces requiring focused, high-intensity lighting.
-
Low Bay: Works best in areas needing uniform lighting at a lower intensity.
Based on their lighting characteristics, high and low bay lights serve different functional needs. High bay lights are ideal for spaces requiring focused, high-intensity lighting, such as warehouses, manufacturing plants, and gymnasiums. Low bay lights excel in areas where uniform, low-intensity lighting is needed, such as retail stores, garages, and storage rooms.
Beam Angle and Light Distribution
-
High Bay: Narrower beam angles to concentrate light downward.
-
Low Bay: Wider beam angles for broad, even coverage.
Lumen Output
-
High Bay: High lumen output to counteract distance from the ceiling.
-
Low Bay: Moderate lumen output sufficient for closer distances.
Lumen output is tailored to the lighting needs of each ceiling height. High bay lights deliver high lumen output to counteract the distance from the ceiling to the illuminated area, ensuring adequate brightness at ground level. In contrast, low bay lights produce moderate lumen output, which is sufficient for shorter distances in spaces with lower ceilings.
Fixture Types and Design
The designs of high bay and low bay fixtures reflect their specific applications. High bay lights often come in UFO, linear, or round configurations and are frequently paired with reflectors or lenses to direct light effectively and minimize glare. Low bay lights typically feature compact fixtures with diffusers to provide softer, more even illumination suitable for smaller, enclosed spaces.
-
High Bay:
-
UFO, linear, or round designs.
-
Often paired with reflectors or lenses to direct light effectively.
-
Low Bay:
-
Compact fixtures with diffusers for softer, even illumination.
Cost and Energy Efficiency
Cost and energy requirements differ significantly between high and low bay lights. High bay lights generally involve a higher upfront cost due to advanced optics, higher wattage, and their ability to illuminate larger areas. Conversely, low bay lights are more cost-effective for spaces with lower ceilings, offering reduced wattage and simpler designs that meet the needs of smaller environments.
-
High Bay: Typically higher upfront cost due to advanced optics and higher wattage.
-
Low Bay: More cost-effective for spaces with lower ceilings and reduced lighting demands.
| Feature | High Bay Lights | Low Bay Lights |
| Ceiling Height | 20-45+ feet | Below 20 feet |
| Lumen Output | High to compensate for height | Moderate due to closer proximity to the floor |
| Beam Angle | Narrow for more focused illumination | Wide for even coverage |
| Applications | Warehouses, factories, arenas, etc. | Retail, offices, garages, classrooms, etc. |
| Light Types | UFO, linear designs, high bay bulbs, corn bulbs, etc. | Strip light fixtures, panel lights, wraparound fixtures, troffers, LED retrofit kits, etc. |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced optics | Lower upfront cost |
Choosing the Right Bay Lighting
Selecting the appropriate bay lighting is essential for achieving optimal illumination and efficiency in your space. Here’s how to make an informed choice based on key factors and practical examples.
Factors to Consider
-
Ceiling Height and Room Dimensions: The ceiling height determines whether high bay or low bay lights are suitable, while room size influences the number of fixtures and their placement.
-
Desired Light Intensity and Distribution: High bay lights are ideal for focused, high-intensity lighting, while low bay lights provide even, dispersed illumination for smaller spaces.
-
Specific Industry or Application Requirements: Different settings, such as warehouses, retail stores, or gyms, have unique lighting needs that influence the choice of fixture type and design.
Bay Lighting Examples
-
High Bay Example: A warehouse with a 30-foot ceiling requires high bay lights with narrow beam angles to deliver bright, targeted illumination for high shelving and work areas.
-
Low Bay Example: A retail store with a 15-foot ceiling benefits from low bay lights with wider beam angles. These lights provide uniform lighting that enhances product visibility and creates an inviting atmosphere.
Selecting the right bay lighting is crucial for achieving effective and efficient illumination in any space. Proper lighting enhances safety, visibility, and productivity, making it a critical component of any commercial or industrial environment.